The BoE and ECB render the US bond market the only game in town
Now that the Bank of England has commenced purchases of gilts and committed to a programme of corporate bond buybacks, alongside similar measures being presently undertaken by the ECB, it is worth taking a step back and thinking about valuations in sterling fixed income.
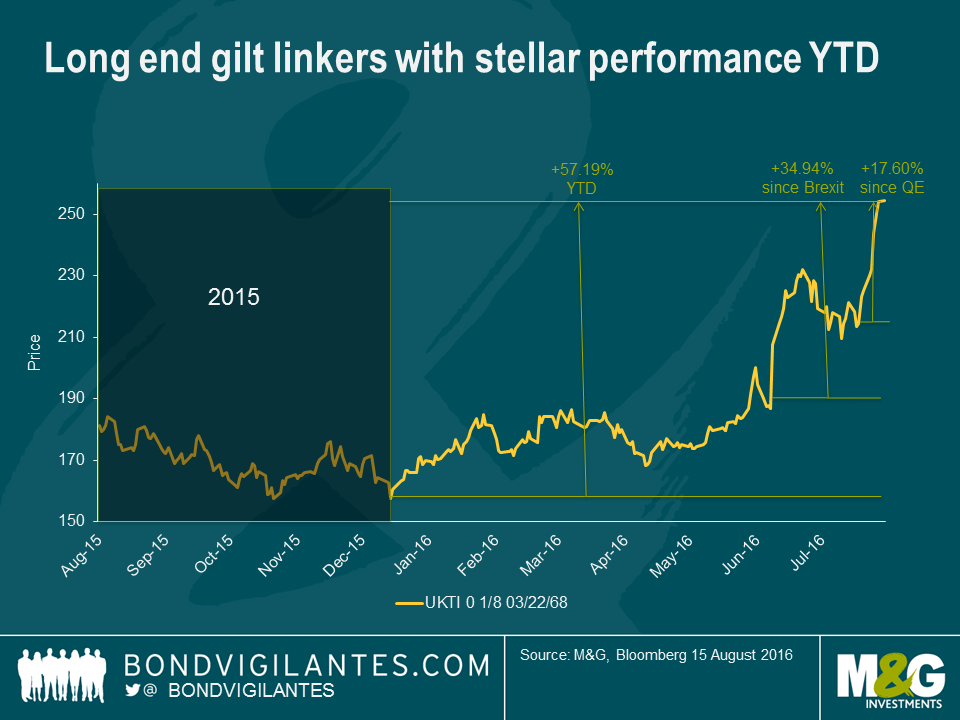
Let’s take a brief look at what has happened so far in 2016 in government bonds. The ultra-long conventional gilt has returned a staggering 52% this year. Since the result of the referendum became clear, the bond’s price has increased by 20%, and in the couple of weeks since Mark Carney announced the Bank of England’s stimulus package, the bond’s price has risen by a further 13%.
But this is not even the top performing government bond of 2016. That mantle goes to the 2068 index-linked gilt, which has seen its price rise by 57% year-to-date, by 35% since the vote to exit Europe, and by 18% since further quantitative easing was announced by the central bank. Interestingly, too, the superior price action of the index-linked bond has occurred not as a result of rising inflation or expectations of inflation; instead it has been in spite of significantly falling inflation expectations so far this year. The driver of the outperformance is solely due to the much longer duration of the linker. Its duration is 19 years longer than the nominal 2068 gilt, by virtue of its much lower coupon!
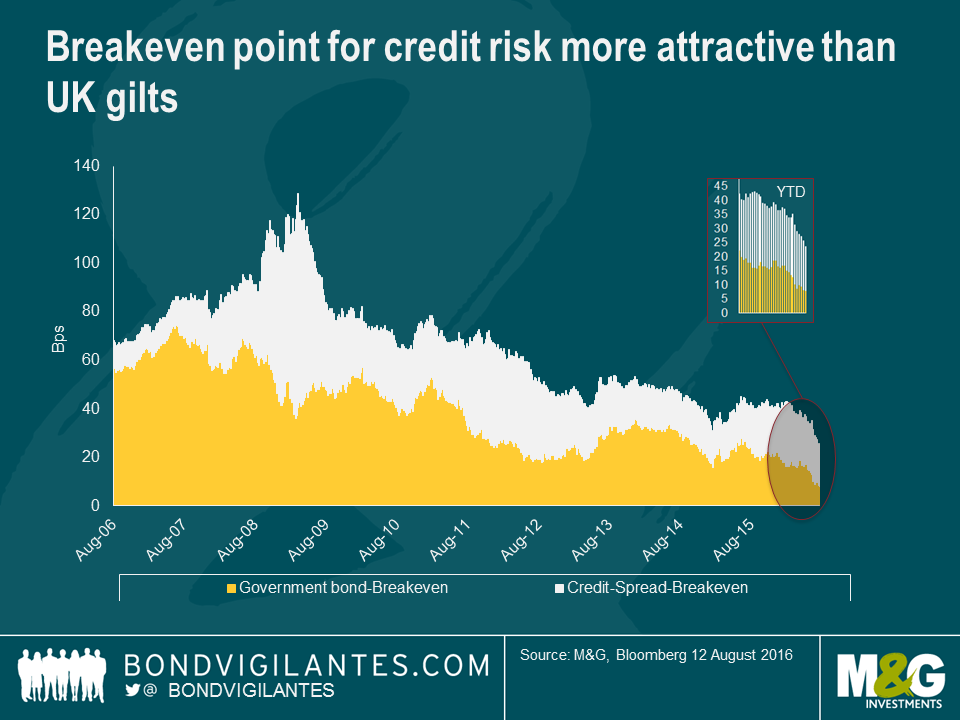
When you buy a corporate bond you don’t just buy exposure to government bond yields, you also buy exposure to credit risk, reflected in the credit spread. The sterling investment grade sector has a duration of almost 10 years, so you are taking exposure to the 10 year gilt, which has a yield today of circa 0.5%. If we divide the yield by the bond’s duration, we get a breakeven yield number, or the yield rise that an investor can tolerate before they would be better off in cash. At the moment, as set out above, the yield rise that an investor in a 10 year gilt (with 9 year’s duration) can tolerate is around 6 basis points (0.5% / 9 years duration). Given that gilt yields are at all-time lows, so is the yield rise an investor can take before they would be better off in cash.
We can perform the same analysis on credit spreads: if the average credit spread for sterling investment grade credit is 200 basis points and the average duration of the market is 10 years, then an investor can tolerate spread widening of 20 basis points before they would be better off in cash. When we combine both of these breakeven figures, we have the yield rise, in basis points, that an investor in the average corporate bond or index can take before they should have been in cash.
With very low gilt yields and credit spreads that are being supported by coming central bank buying, accommodative policy and low defaults, and a benign consumption environment, it is no surprise that corporate bond yield breakevens are at the lowest level we have gathered data for. It is for these same reasons that the typical in-built hedge characteristic of a corporate bond or fund is at such low levels. Traditionally, if the economy is strong then credit spreads tighten whilst government bond yields sell off, such as in 2006 and 2007. And if the economy enters recession, then credit spreads widen and risk free government bond yields rally, such as seen in 2008 and 2009.
With the Bank of England buying gilts and soon to start buying corporate bonds, with the aim of loosening financial conditions and providing a stimulus to the economy as we work through the uncertain Brexit process and outcome, low corporate bond breakevens are to be expected. But with Treasury yields at extreme high levels out of gilts, and with the Fed not buying government bonds or corporate bonds at the moment, my focus is firmly on the attractive relative valuation of the US corporate bond market.
The value of investments will fluctuate, which will cause prices to fall as well as rise and you may not get back the original amount you invested. Past performance is not a guide to future performance.


18 years of comment
Discover historical blogs from our extensive archive with our Blast from the past feature. View the most popular blogs posted this month - 5, 10 or 15 years ago!

Bond Vigilantes
Get Bond Vigilantes updates straight to your inbox