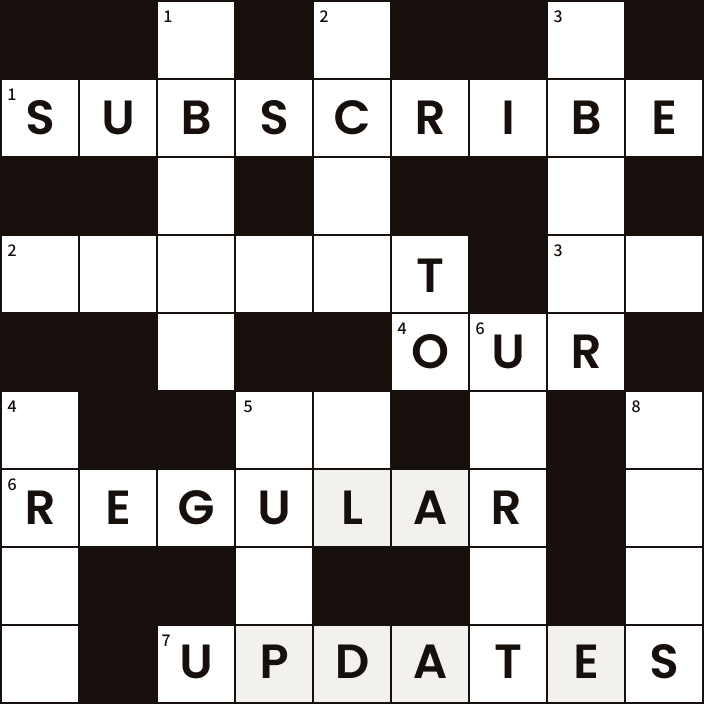America’s great build-a-thon comes with a price tag
The United States is on the brink of an industrial transformation that could redefine its economic trajectory. Inward investment is surging, driven by a wave of new manufacturing plants, onshoring and reshoring initiatives, and a parallel boom in data centre and power generation construction. This is not incremental change; it is a structural shift that will demand vast amounts of labour, raw materials, and productive capacity. The question for investors and policymakers is whether this investment renaissance will reignite inflationary pressures which might lead to a newly reconstituted Federal Reserve signalling a willingness to run the economy “hot”.

The scale of manufacturing investment alone is extraordinary. Semiconductor fabrication plants, battery gigafactories, and advanced automotive plants are being announced at a pace unseen in decades. Industry estimates suggest that annual construction outlays for manufacturing could exceed an estimated $250 billion1 in both 2026 and 2027, as companies seek to localise and secure supply chains. These projects are not confined to the technology sector; they span electronics, pharmaceuticals, and heavy industry, creating a broad-based surge in demand for skilled labour and specialised materials. This manufacturing wave is additive to the already intense pressure from hyperscale data centre construction, which has become a defining feature of the digital economy. With AI and cloud computing hyperscalers expected to drive driving unprecedented demand for processing power, data centre investment is projected to account for half of the projected $1.2 trillion2 global data centre capital expenditure by 2029, while power generation projects will similarly scramble to keep pace with the energy requirements of this new infrastructure which are forecast to more than double over the next 10 years.3
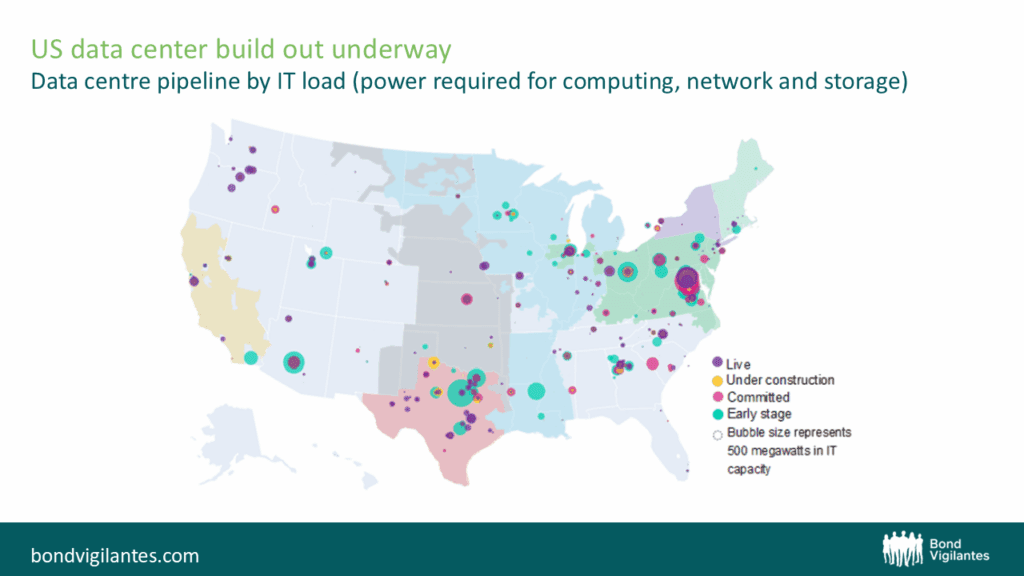
Source: DC Byte, Bloomberg NEF. Reported as of 15/04/2025. IT capacity is the amount of power a data centre needs for computing, network and storage
The implications for the labour market are huge. The construction sector already faces a shortfall of nearly half a million workers, and the competition for skilled trades, engineers, and project managers will only intensify as manufacturing and technology projects converge. Wage inflation is inevitable. In hotspots where multiple megaprojects collide, wage growth could easily outstrip national averages, creating ripple effects across the broader economy. Immigration constraints and demographic trends exacerbate the problem, and will leave employers with few options beyond aggressive pay increases and retention incentives. This is not a temporary squeeze; it is a structural challenge that will persist as long as the investment pipeline remains full.
Raw materials tell a similar story. Steel, aluminium, copper, and cement are all set to experience sustained demand shocks as the buildout progresses. Tariffs and supply chain fragmentation have already pushed input costs higher, and the synchronised surge in construction activity will amplify these pressures. Equipment lead times are lengthening, and logistical bottlenecks remain unresolved. The result is a cost base that is not just rising but likely to sharply accelerate, with regional disparities adding complexity for project planners and investors alike.
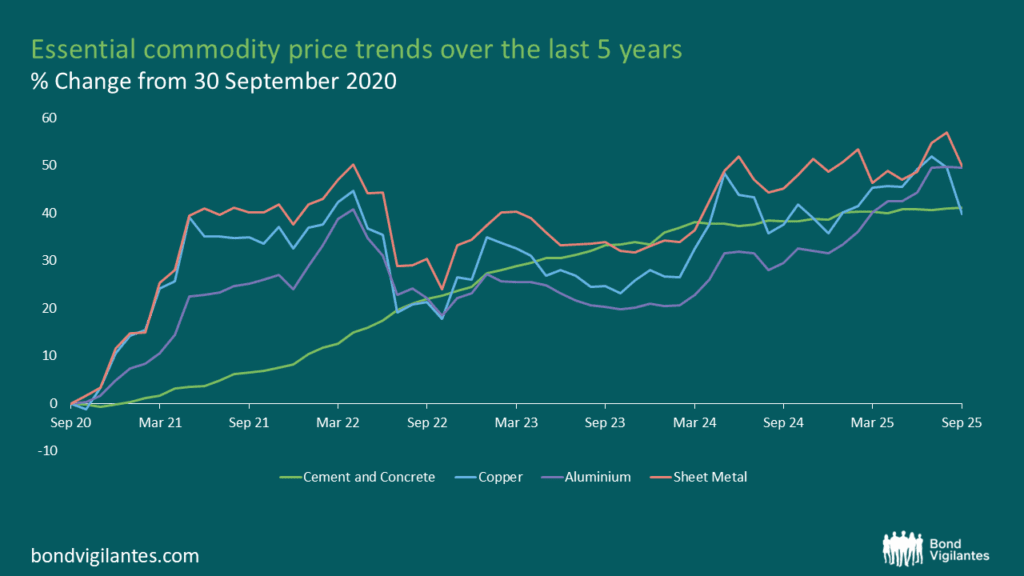
Source: Bloomberg, Bureau of Labour Statistics
Overlay this with monetary policy, and the picture becomes even more concerning . The Federal Reserve has signalled a more accommodative stance for some time, tolerating inflation above its long-term target in the interest of sustaining growth and employment. This willingness to let the economy run hot serves a dual purpose: lower rates support the industrial build-out and, as a by-product, higher inflation erodes the real value of the US government’s $38 trillion4 debt mountain. For policymakers, this is a calculated risk; for bond investors, it is a warning shot. A period of elevated inflation may be politically palatable and even strategically desirable, but it comes at the expense of real returns and introduces volatility into rate expectations. If the Fed cuts too aggressively while fiscal incentives continue to flow, the combination of easy money and surging real-economy demand could create a perfect storm for inflation in 2026 and 2027.
The broader macroeconomic consequences are clear. A synchronised boom in manufacturing, data centres, and power generation will strain every aspect of productive capacity. Labour markets will tighten further, wages will rise, and material costs will climb. These sector-specific pressures will bleed into headline inflation, challenging the narrative of a smooth return to price stability. For investors, the message is simple: the risk premium for inflation is back, and positioning for real assets, pricing power, and inflation-linked instruments will be critical. For policymakers, the challenge is to harness the benefits of reindustrialisation without igniting an inflationary spiral that undermines financial stability.
America’s great build-out will test the limits of labour supply, material availability, and monetary policy flexibility. If the Fed remains tolerant and the economy runs hot, the debt mountain may shrink in real terms—but so too will the purchasing power of every dollar in circulation. For bond investors this industrial renaissance may be good for growth, but it could also be the spark that reignites inflationary fire.
1 US Census Bureau, FERC, BEA EIA estimates
2 Dell’Oro Group, August 2025
3 Power for AI: Easier Said Than Built | BloombergNEF
4 US Treasury Department, November 2025
The value of investments will fluctuate, which will cause prices to fall as well as rise and you may not get back the original amount you invested. Past performance is not a guide to future performance.